A Few Examples of Pictures (Using MATLAB or c++):
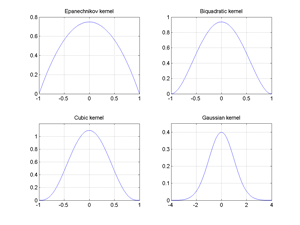
Fig. Epanechnikov, Biquadratic, Gaussian and Cubic kernels.
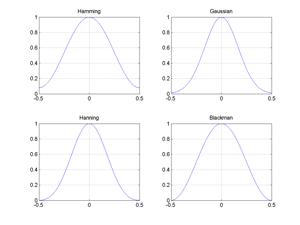
Fig.5.24 Hamming, Gaussian, Blackman, Hanning windows.
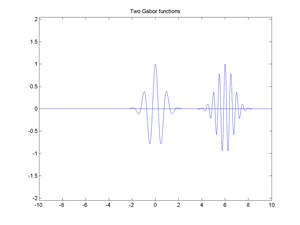
Fig.5.3 Two Gabor functions (also named Gabor atoms).
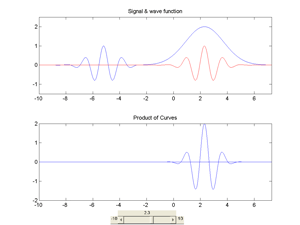
Fig.5.11 Convolution of an arbitrary signal with a wave function which moves along the signal. A convolution of two functions f and g can be written for instance as follows: f • g= ∫ [g(s) f(t-s)] ds.
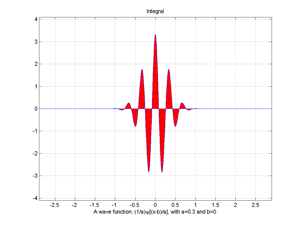
Fig.5.4 Area of a wave function.
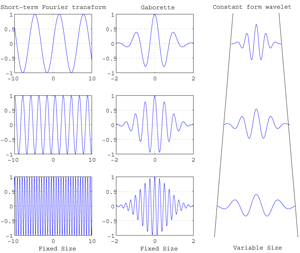
Fig.5.10 Distinction of the different window mechanisms by type of Transformation. Types of transformation: 1.Short-term Fourier: Fixed size, 2.Gabor function: Fixed size, 3.Constant form wavelet: Variable size.
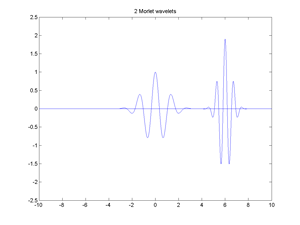
Fig.5.7 Two Morlet Wave functions.
